PCIE interface
overview
1. PCIE (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard used to connect computer motherboards and various peripherals, such as graphics cards, solid state drives, network cards, etc. It replaces the traditional PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) interface and offers a huge improvement in performance and functionality.
Physical characteristics
1. Multiple specifications
1. PCIE interfaces are available in a variety of different lane configurations, including x1, x4, x8, and x16, among others. The number after the "x" indicates the number of channels. For example, PCIE x1 has 1 lane and PCIE x16 has 16 lanes. These different sizes of connectors differ in length and number of pins. The PCIE x1 interface is shorter and has fewer pins, making it mainly used in some devices with lower bandwidth requirements; PCIE x16, on the other hand, has a longer interface and more pins, and is typically used in high-performance devices such as graphics cards.
2. Matching of slots and cards
1. The interface cheat part of the device (such as an expansion card) matches the slot on the motherboard. For example, a PCIE x1 card can only fit into a PCIE x1 slot, while a PCIE x16 card generally needs to be plugged into a PCIE x16 slot, but some motherboards have a PCIE x16 slot that is also compatible with x8, x4, or even x1 devices, depending on the design of the motherboard and the BIOS settings.
Transmission characteristics
1. Serial transmission mode
1. UNLIKE THE PARALLEL TRANSMISSION OF TRADITIONAL PCI INTERFACES, PCIE USES SERIAL TRANSMISSION. In this way, data can be transmitted at a high frequency on each channel, reducing signal interference and transmission errors. For example, in parallel transmission, the simultaneous transmission of multiple signals can create crosstalk, which is avoided by serial transmission.
2. High bandwidth
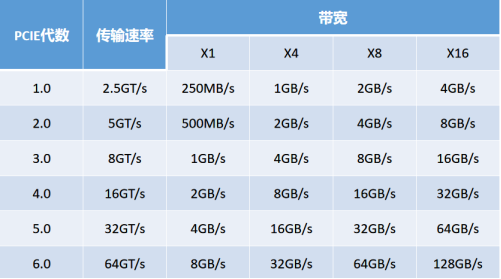
1. Each PCIE lane has a certain bandwidth, and as the technology develops, the bandwidth continues to increase. For example, under the PCIE 3.0 specification, each lane can have a unidirectional bandwidth of about 1GB/s and a bidirectional bandwidth of about 2GB/s. PCIE 4.0 doubles the unidirectional bandwidth to about 2GB/s per lane and 4GB/s bidirectionally. FOR PCIE x16 INTERFACES, THE THEORETICAL BANDWIDTH CAN REACH ABOUT 32GB/S (ONE-WAY) UNDER PCIE 3.0 AND ABOUT 64GB/S (ONE-WAY) UNDER PCIE 4.0.
3. Low latency
1. The PCIE interface has a low transmission latency and is able to quickly transfer data from the device to the computer system or vice versa. This is important for devices that require real-time response, such as high-performance NICs and graphics cards. Taking a gaming graphics card as an example, low latency can ensure that the game screen can be displayed quickly and smoothly, reducing screen lag and stuttering.
Application scenarios
4. Graphics card connection
1. In computers, graphics cards are usually connected to the motherboard using the PCIE x16 interface. This is because the graphics card requires high bandwidth to transfer a large amount of graphics data, such as texture data, vertex data, etc. For example, when running 3D games or professional graphics software such as 3DMAX, Photoshop, etc., the graphics card performs high-speed data exchange with the CPU and memory through the PCIE interface to achieve high-quality graphics rendering.
5. Solid-state drive (SSD) connection
1. Some high-performance SSDs use PCIE interfaces, especially NVMe protocol SSDs with M.2 interfaces, and some achieve high-speed data transmission through PCIE lanes. PCIE INTERFACE SSDS CAN PROVIDE HIGHER READ AND WRITE SPEEDS THAN TRADITIONAL SATA INTERFACE SSDS. For example, the PCIE 3.0 x4 interface can easily exceed 3000MB/s of SSD sequential read speeds, and sequential write speeds can also reach a very high level, greatly improving the boot speed of the system and the loading speed of applications.
6. Network card connection
1. High-speed network cards, such as 10 Gigabit network cards, will also use PCIE interfaces. FOR SERVERS OR HIGH-END DESKTOPS THAT REQUIRE LARGE AMOUNTS OF NETWORK DATA TRANSFER, A PCIE INTERFACE NETWORK CARD CAN PROVIDE ENOUGH BANDWIDTH TO ENSURE FAST DATA TRANSFER. For example, in a server in a data center, a network card with a PCIE interface can efficiently handle a large amount of network traffic and ensure high-speed communication between servers.
7. Other Expansion Devices
DEVICES INCLUDING SOUND CARDS, VIDEO CAPTURE CARDS, USB 3.0/3.1 EXPANSION CARDS, AND OTHER DEVICES CAN ALSO USE THE PCIE INTERFACE. For example, a standalone sound card can provide better audio processing performance through the PCIE interface, meeting professional needs such as music production and audio editing. The video capture card can quickly acquire external video signals into a computer for processing via the PCIE interface.


